Introduction
As technology continues to transform business rapidly, blockchain technology is seen as transforming the dynamics of supply chain management, enabling companies to track and secure their operations more effectively. Most traditional and existing supply chain management systems face issues regarding transparency, traceability, and real-time data sharing, which generate billions of losses for companies worldwide.
Blockchain technology in the supply chain is a revolutionary innovation that makes records and transactions fully immutable and transparent. As the new supply chain solution is driven by blockchain, things go far beyond record keeping to a whole new level. With supply chains continuing to expand globally, developing blockchain for logistics presents a definite and clearly slated system that can promote more cooperation between manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, and retailers.
The blockchain in the supply chain comes at the right time when consumers are increasingly conscious of the sources of the products they use. Firms, companies, and organizations are struggling to fight fraud and counterfeit products and methods to track and monitor their supply chains cheaply and effectively.
Purpose of the Blog
This blog delves into various aspects of the supply chain revolution and how blockchain solutions are changing traditional operations. It provides insights from practice into blockchain-enabled systems in supply chains and shows the businesses that can benefit from using this technology to improve efficiency and transparency.
Blockchain supply chain optimization is a fundamental change in the way businesses run their operations. As the adoption of blockchain supply chain tracking continues to grow worldwide, organizations need to be aware of how it can transform their processes, increase security, and build customer trust by enhancing transparency.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Definition of Blockchain
The application of blockchain in the supply chain is an Internet-based system of recording multiple transactions across several computers, which is completely safe and transparent. Imagine it as data blocks, and each new record brought means that the chain is never interrupted and offers an entirely new concept of how supply chains should work.
- This means that data flows through the chain in the manner that cars move through one-way streets.
- For every computer in a network they have identical records as the other computer in the network.
- Special codes connect each block, thereby forming an information chain.
- To add other information blocks to the network’s structure, network members must make certain decisions.
- Security measures take care of all the stored data from being edited by unauthorized people.
Core Features
Decentralization
In blockchain for logistics, no single organization controls the system. However, all information is coordinated and moderated through a network of participants, providing actual democracy and openness for the supply chain activities.
- The degree of freedom and the collective responsibility of network participants in the validation of the supply chain data is equal.
- Duplicates are against single points of system failure.
- The study postulates that an optimal level of supply chain control involves joint management by supply chain members, with this increased control leading to higher levels of trust between supply chain parties.
Immutability
Once data enters the blockchain-enabled supply chain, it becomes permanent and unchangeable. This way, product tracking information, shipping records, or transaction records will always be trustworthy and accurate for eternity.
- Documents endure forever, as we say, writing on the wall.
- To make changes, new blocks must be generated while history remains preserved.
- Data integrity is preserved from external interferences and unauthorized alteration.
Transparency
Blockchain supply chain transparency allows all authorized participants to view the same information simultaneously. This shared visibility helps prevent disputes and enables better collaboration across the supply chain revolution.
- All get to view the information at the same time.
- Follow the product to go through manufacturing and find a place on the shelf.
- The audit trails help partners be more accountable.
Security
Advanced encryption and consensus mechanisms make blockchain supply chain tracking highly secure. This protection ensures that sensitive business data stays safe while enabling efficient supply chain optimization with blockchain.
- All collected data is insured by highly developed math.
- Several barriers of security help to prevent intruders from accessing sensitive data or information.
- Implementation concerning change in the network requires an agreement for the addition of new information.
Key Blockchain Components
Blocks
In decentralized supply chain management, blocks serve as digital containers for important transaction data. Each block usually records a large number of facts about shipments, payments, or products moving through the chain from one or more vendors.
Chain
For blockchain applications in the supply chain, the chain links all the blocks and records every transaction made. This unbroken sequence guarantees that information continues to pass through the whole system at regular intervals.
Nodes
Smart contracts in the supply chain rely on nodes, which are computers that validate and record transactions. They operate to perform the activity and exist to keep the network of the news and all related information precise.
Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology in logistics management uses smart contracts to automate agreements. When certain conditions are met, these contracts immediately execute contract provisions, facilitating the supply chain.
The Challenges of Traditional Supply Chain Management
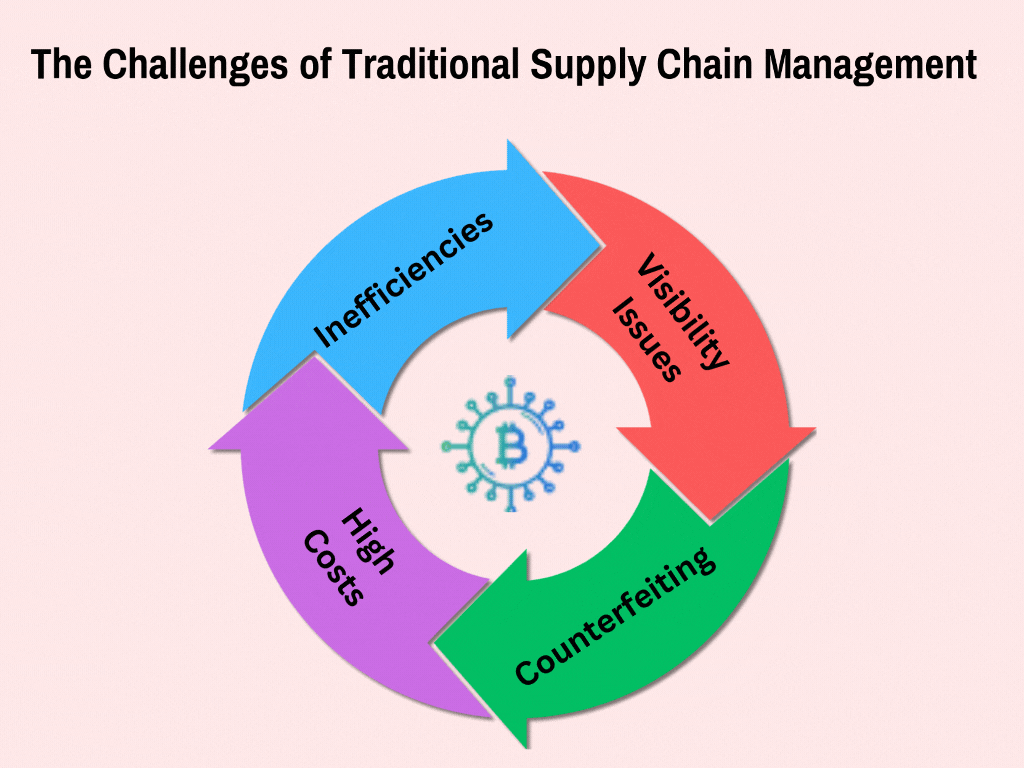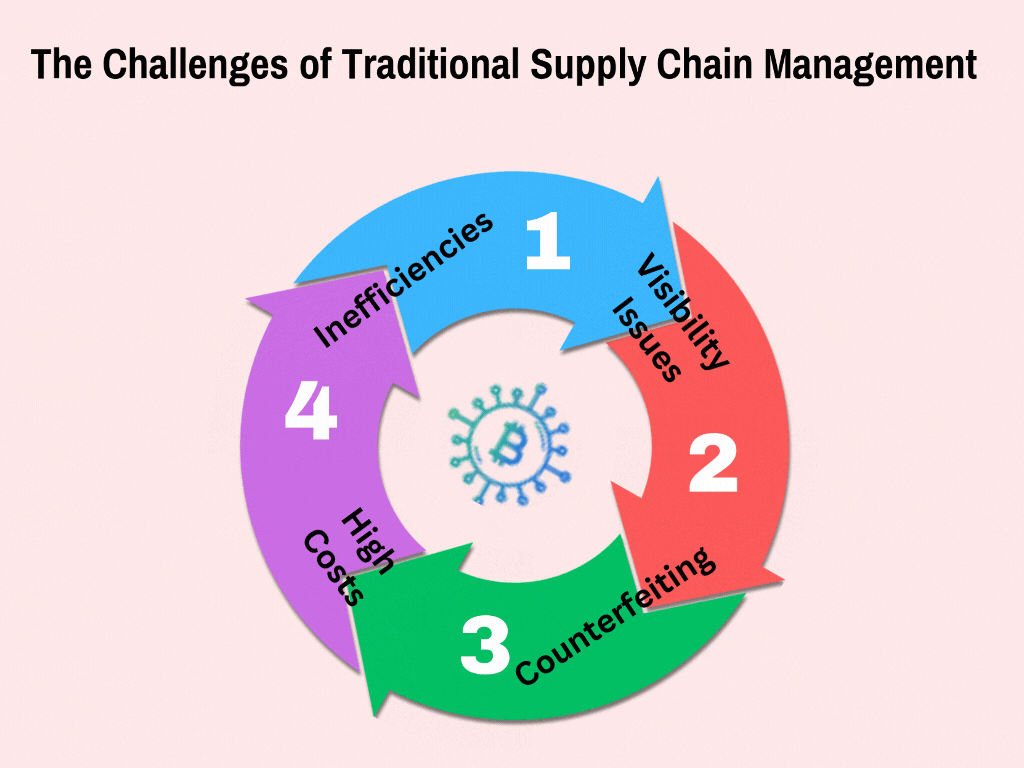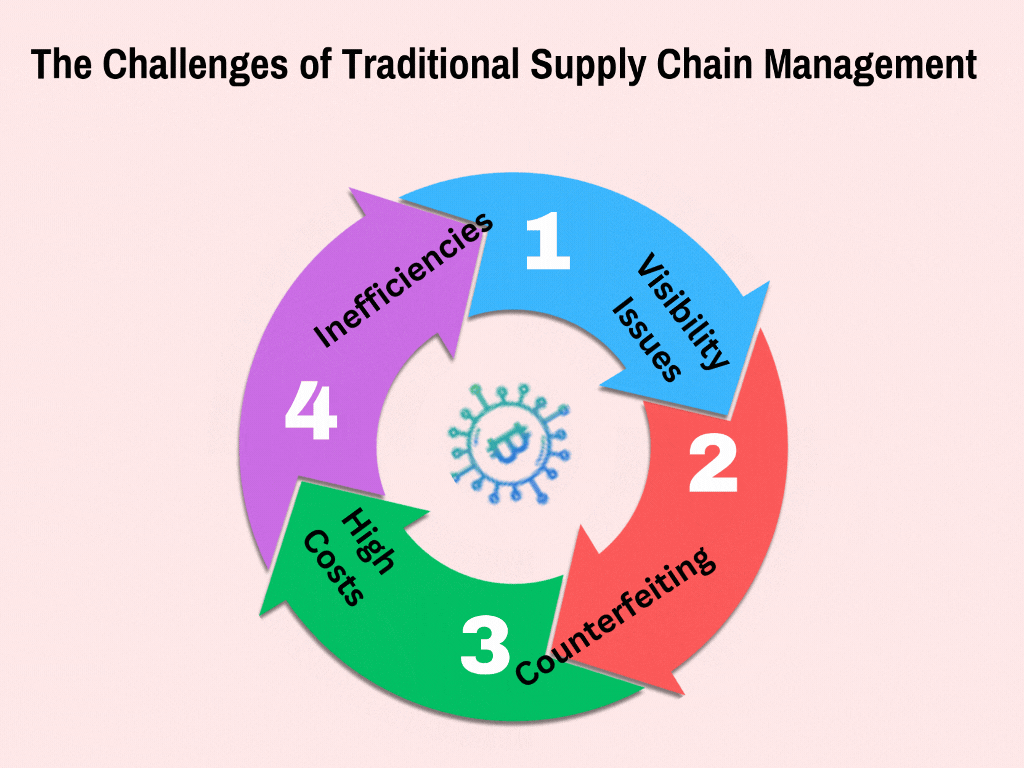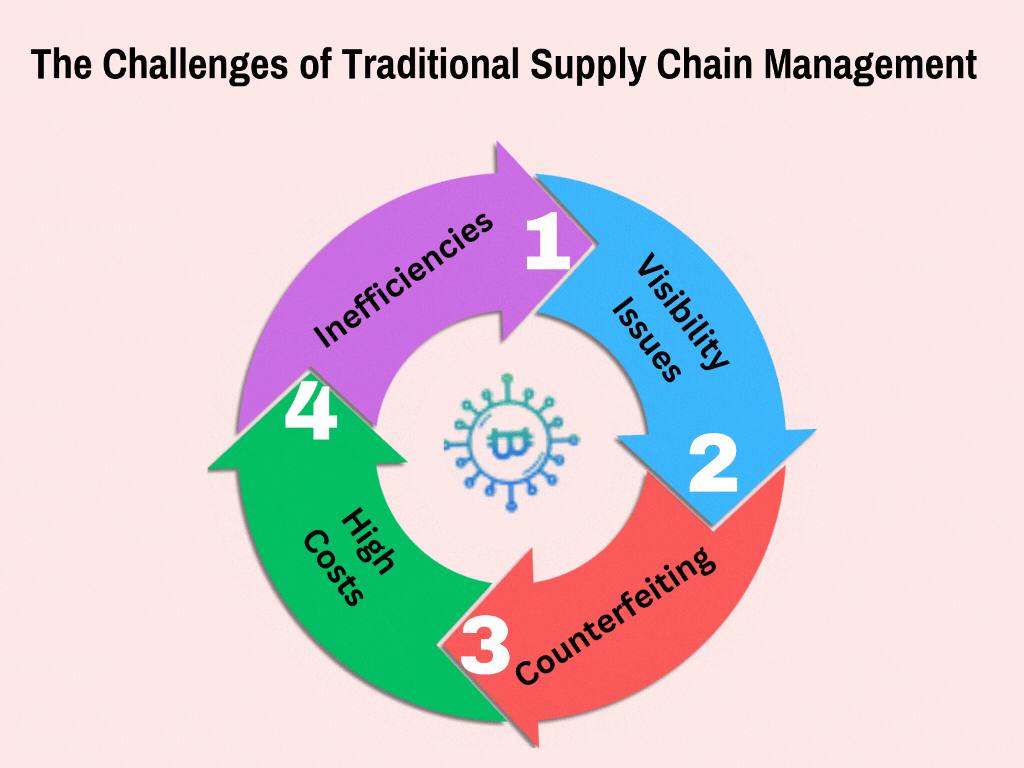
Inefficiencies and Delays
Traditional supply chain management often feels like a complicated game of telephone, with messages getting mixed up along the way. Managers continue to use paper and manually input data into the system, thus making expensive errors and taking a lot of time. Before blockchain for logistics transformed the industry, tracking shipments in real time was nearly impossible, and making quick decisions was highly challenging.
Fraud and Counterfeiting
The supply chain revolution couldn’t come soon enough, as traditional systems struggle with authenticity verification. Without soundtracking methods, counterfeit items can penetrate accredited supply systems. Many firms only realize the presence of counterfeits after they receive many complaints from their customers about unsatisfactory products that have harmed the manufacturers’ reputations. Blockchain technology in the supply chain now offers a powerful solution to this persistent problem.
Visibility Issues
Supply chain management traditionally operates like separate islands of information, with each company seeing only its small piece of the puzzle. Due to this fragmented visibility, it becomes challenging to map a product from the manufacturing plant to the shop shelves. Before blockchain supply chain transparency emerged, companies had no reliable way to verify product origins or track their journey through multiple handlers.
High Costs
The traditional approach to blockchain and inventory management involves numerous middlemen, each adding fees and complexity to the process. Think of it as a toll road: You have to pay when you check a point along the way. These multiple handoffs not only increase costs but also create more opportunities for errors and delays, making supply chain optimization with blockchain an attractive alternative.
How Blockchain is Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management
Improved Transparency and Traceability
End-to-End Tracking
Blockchain supply chain tracking creates a complete digital trail of every product’s journey. Picture being able to track your parcel from the factory through the transport system and finally to the doorstep. Blockchain technology enables this level of tracking, and it is not hard to achieve.
Provenance Tracking
Blockchain’s ability to verify product origins is revolutionizing supply chain management. Each item receives an embedded URL to an original certificate that cannot be forged. This means that companies can be sure that some of the products they sell are authentic and have been sourced and produced correctly.
Consumer Confidence
The supply chain revolution empowers consumers to verify product authenticity instantly. With blockchain in supply chain systems, shoppers can use their smartphones to scan a product and see its entire life cycle, from raw material to the end product, hence creating so much trust.
Enhanced Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Automation with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts in the supply chain work like digital assistants that automatically handle payments and paperwork. Since the release of payment and records is automatically generated whenever a shipment of goods is made through a truck, they are much faster and cheaper.
Faster Processing
This is because using blockchain in the supply chain reduces the time needed to operate. Instead of waiting days for paperwork to process, blockchain-enabled supply chain systems can complete transactions and verify information almost instantly.
Error Reduction
Blockchain for logistics virtually eliminates manual data entry mistakes. The information is checked and verified systematically, thereby minimizing costly mistakes that such systems are well known to cause in supply chains and slow down the process.
Strengthened Security
Cryptographic Protection
Blockchain technology in logistics management uses advanced mathematical codes to protect information. It’s like an encrypted treasure chest with a limited number of keys, where all the business information is stored safely.
Immutable Ledger
Supply chain optimization with blockchain ensures that once information is recorded, it cannot be changed or deleted. This affords a means of creating a permanent record-keeping system that eliminates fraud and data integrity distortion in supply chain records.
Decentralization
Decentralized supply chain management spreads control across many computers instead of storing everything in one place. This distribution makes it very hard for hackers to compromise the system independently.
Optimized Inventory Management and Demand Forecasting
Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Blockchain and inventory management work together to provide instant updates on stock levels. Products in the shops and the company’s stock can be traced, avoiding losses due to stockouts and having many unsold goods.
Demand Forecasting
Blockchain solutions for supply chains enable better predictions of future needs. Transparent goods flow helps businesses identify buyers and prepare for the subsequent demand.
Integration with IoT
Blockchain supply chain transparency reaches new heights when combined with smart sensors. These sensors also track the conditions of all products and periodically and autonomously send data changes to the blockchain, enhancing the quality control process.
Real-world Applications of Blockchain in Supply Chains
Case Study 1: Walmart’s Use of Blockchain for Food Safety
Implementation
Walmart revolutionized supply chain management by implementing blockchain technology through IBM’s Food Trust platform. This system keeps records of all the stages a food product goes through, from the farm to the supermarket shelf. It further highlights this by assigning each item a unique identification number that captures its entire history.
Results
Walmart’s blockchain for logistics reduced the time it takes to trace food origins from seven days to just 2.2 seconds. In food recalls, stores can now immediately remove the products, which can be especially important in saving lives and sharply reducing food waste.
Case Study 2: Maersk and TradeLens—Revolutionizing Shipping
Implementation
The supply chain revolution gained momentum when Maersk launched TradeLens, showcasing powerful blockchain applications in supply chain management. This platform transforms documents and establishes Central Records, a secure repository of all shipping containers and documents across oceans and borders.
Results
Through blockchain-enabled supply chain solutions, Maersk reduced administrative costs by 15% and shipping times by 40%. What used to take days to process documentation can now be done in minutes.
Case Study 3: De Beers—Blockchain for Ethical Sourcing of Diamonds
Implementation
Through its Tracr platform, De Beers transformed its operations through supply chain optimization with blockchain. This decentralized supply chain management system creates a permanent digital record for each diamond, tracking it from mine to retailer.
Results
Blockchain supply chain transparency helped De Beers virtually eliminate conflict diamonds from its supply chain. Thus, consumer trust rose significantly as purchasers could quickly establish their diamond’s origins.
Insight
These real-world examples demonstrate how blockchain technology in logistics management is creating tangible benefits:
- Faster product tracking and verification
- Reduced operational costs and paperwork
- Enhanced consumer trust through transparency
- Improved safety and quality control
- Streamlined international trade processes
Each case study shows different aspects of how blockchain supply chain tracking is transforming traditional business operations into more efficient, transparent, and trustworthy systems.
The Key Benefits of Blockchain for Supply Chains
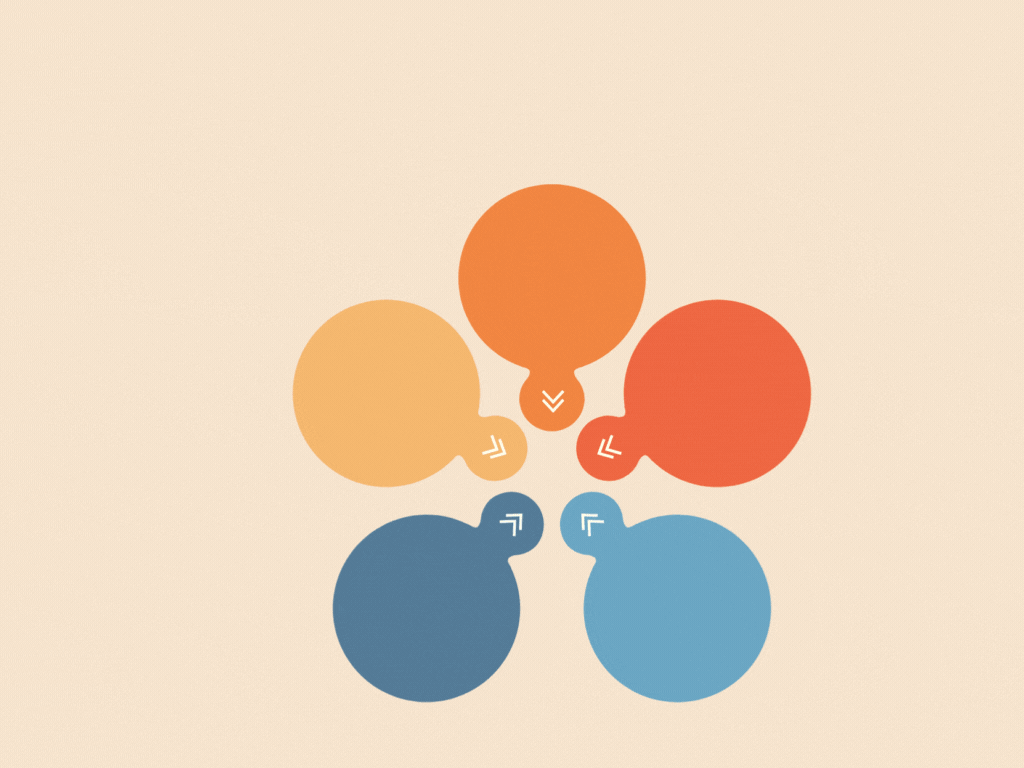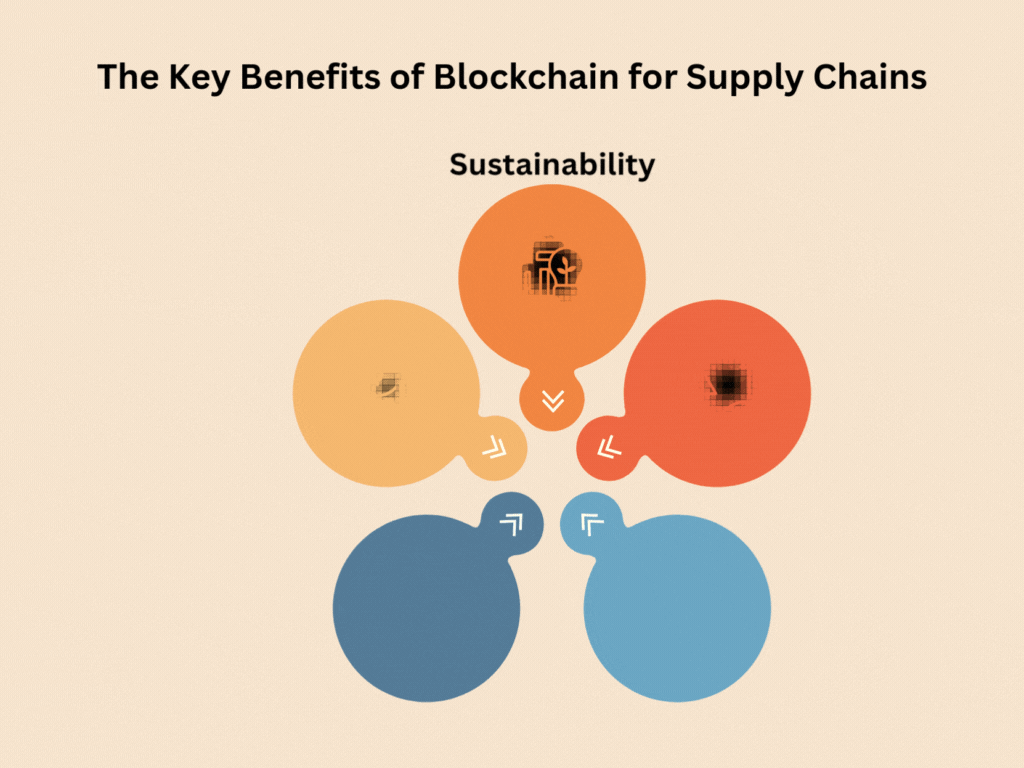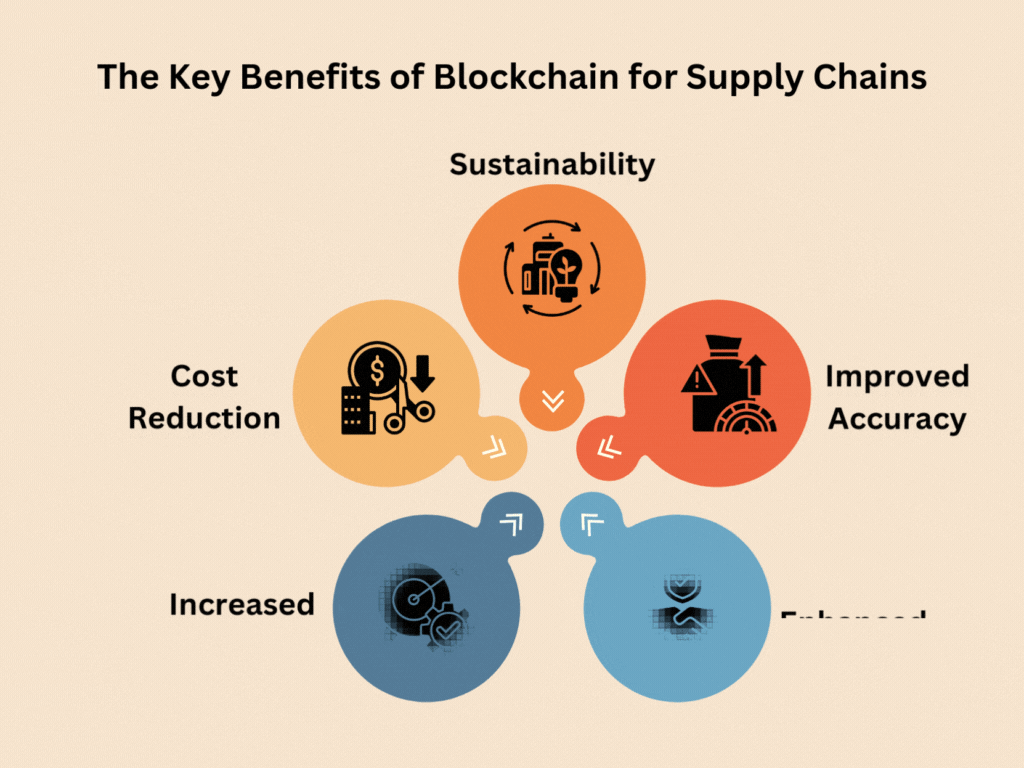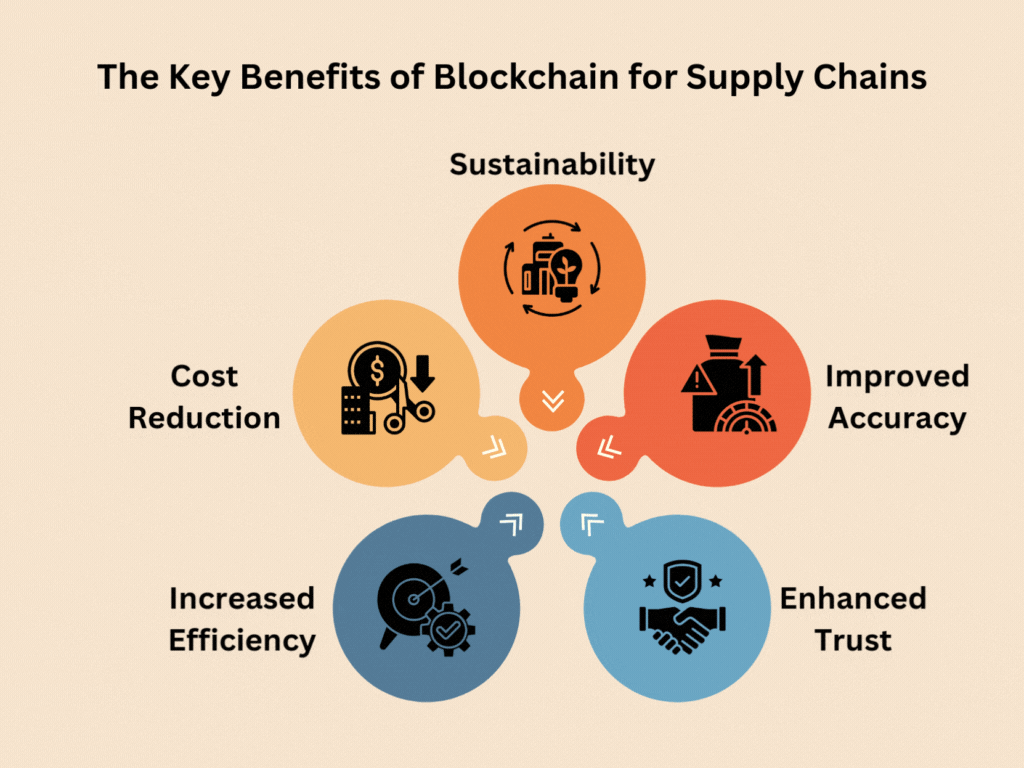
Increased Efficiency
Through blockchain technology, the complex and time-consuming manual activities in the supply chain are made to appear seamless. You have to remember that one has to change a piece of paper with directions to a GPS—everything becomes faster and more accurate. Supply chain management tasks that once took days now happen automatically in seconds, thanks to smart contracts that eliminate unnecessary intermediaries.
Cost Reduction
The supply chain revolution driven by blockchain significantly reduces expenses across operations. Rather than paying multiple parties to verify and process transactions, blockchain-enabled supply chain systems handle these tasks automatically. Imagine cutting out all the toll booths on a highway—that’s how blockchain for logistics streamlines costs.
Improved Accuracy and Accountability
Blockchain supply chain tracking creates an unbreakable chain of information that records every step in a product’s journey. Unlike a fingerprint, the domain part of an email address cannot be altered once it is created. Blockchain applications track all actions that take place in the supply chain, making it difficult to determine who did what.
Enhanced Trust
Blockchain supply chain transparency revolutionizes how businesses and customers trust each other. Through decentralized supply chain management, everyone can verify product authenticity and history. It’s like having a kind of glass that, when you look into it, shows you how your product got to you.
Sustainability
Supply chain optimization with blockchain helps protect our planet by making it easier to verify eco-friendly practices. Through precise blockchain and inventory management systems, companies can more accurately track their environmental impact, from monitoring carbon footprints to reducing waste. This technology assists companies in making improved decisions regarding their operations, profits, and environmental concerns.
Insight
These benefits demonstrate why blockchain technology in logistics management has become essential for modern businesses:
- Faster operations with fewer errors
- Lower costs through automation
- Complete traceability of products
- Increased trust between all parties
- Better environmental protection
Together, these advantages make blockchain solutions for supply chains a powerful tool for transforming traditional business operations into more efficient, transparent, and sustainable systems.
Potential Challenges of Adopting Blockchain in Supply Chains
High Initial Investment
While blockchain technology offers impressive benefits in the supply chain, getting started requires substantial funding. Companies must acquire new computer systems, educate their personnel, and reconstruct current processes. These startup costs are highly burdensome to small businesses, especially when they feel like they have to buy a whole fleet of trucks. In reality, they only need a delivery van specific to their business.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Supply chain management systems that have been running for years often struggle to connect with new blockchain solutions. Imagine trying to connect a modern smartphone to a 1980s television—that’s similar to the challenge companies face when implementing blockchain for logistics with their older systems. The supply chain revolution requires careful planning to avoid disrupting daily operations.
Scalability Concerns
As blockchain supply chain tracking grows, processing all transactions quickly becomes challenging. It’s like a highway during rush hour—traffic jams are a consequence of having too much congestion (too many transactions). While blockchain-enabled supply chain systems work well for smaller operations, scaling up to handle millions of transactions requires specialized solutions and careful planning.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The rules governing blockchain technology in logistics management are still developing. Companies investing in decentralized supply chain management face uncertainty similar to driving in a new city without traffic signs. Due to such ambiguities, some organizations may be reluctant to adopt blockchain applications in supply chain management to the extent that is envisaged.
Complexity in Managing Data Across Stakeholders
Supply chain optimization with blockchain requires smooth collaboration among all participants. Think about it in terms of staging a relay and having all the runners know and accept when and how the race is going to be run. Similarly, it can be extremely challenging to get all supply chain partners to adopt compatible blockchain and inventory management systems and agree on data-sharing protocols.
Insight
Common implementation challenges include:
- Technical difficulties in connecting different systems
- Resistance to change from employees and partners
- Time needed to train staff on new processes
- Coordination issues across multiple organizations
- Concerns about data privacy and security
Despite these challenges, many companies find that the benefits of blockchain supply chain transparency outweigh the initial hurdles, leading to more efficient and trustworthy operations in the long run.
The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Increasing Adoption
Major corporations are rapidly embracing blockchain technology in the supply chain, recognizing its potential to revolutionize operations. Blockchains are emerging as a game changer, and many companies, from Walmart to Maersk, are adopting them to optimize their supply chains and create highly efficient and even more integrated systems.
Blockchain and AI Integration
The convergence of blockchain for logistics and artificial intelligence is creating more innovative supply chains. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data, enabling real-time tracking and predictive maintenance while enhancing supply chain management through automated decision-making.
Decentralized Autonomous Supply Chains
The supply chain revolution is leading towards autonomous systems where blockchain-enabled supply chain networks operate independently. This advancement in decentralized supply chain management allows for automated ordering, tracking, and delivery processes with minimal human oversight.
Cross-Border Supply Chains
Blockchain supply chain transparency is transforming international trade. Smart contracts in the supply chain streamline customs processes, while blockchain supply chain tracking ensures products move seamlessly across borders, reducing delays and improving efficiency.
Conclusion
Summary
The concept of blockchain technology in the supply chain is gradually changing the way companies are run. This supply chain revolution enables companies to track products perfectly from start to finish. These developments in the field of blockchain are essential for the future outcome of supply processes and general business functioning.
Future Outlook
The future of supply chain management increasingly depends on blockchain technology. As blockchain for logistics continues to mature, more industries are discovering its benefits for streamlining operations. Increased transparency and efficiency of supply chains are the other impacts of this kind of transformation globally.
Don’t let your business fall behind in the supply chain revolution. Implementing blockchain-enabled supply chain solutions today will prepare your organization for tomorrow’s challenges. Innovative companies are already exploring blockchain solutions for supply chain optimization to stay competitive.
FAQs
How is blockchain technology transforming supply chain management?
Blockchain technology is transforming supply chain management by enhancing transparency and security. It provides all the parties involved in the supply chain of products with accurate, actual information, decreasing cases of fraud and mistakes. Concerning cost and time reduction, smart contracts eliminate procrastination, and the blockchain minimizes paperwork. This makes business transactions quicker and more efficient and enables easy identification and authenticity of goods, easing the whole supply chain and hence reducing costs.
What are the key benefits of using blockchain in supply chains?
The advantages of blockchain in the supply chain are greater visibility, innovation, and better security. This one allows users to get a clear real-time view of all the transactions taking place, thus making it easier to track products and cutting down on fraud activities. Blockchain allows only authorized parties to access the information and has a non-adjustable, non-reversible feature as its core to maintain data authenticity. Blockchain also helps to work through intelligent contracts to avoid using time and monetary resources by machines. Altogether, blockchain assists in improving the supply chain reliability and reducing its costs.
Can blockchain be implemented in small businesses' supply chains?
Indeed, there is evidence that blockchain technology can efficiently be used in the supply chain management of small businesses. It enhances transparency by tracking the movements of goods and preventing issues such as mistakes and embezzlement. Blockchain can also make processes easier by automating small activities such as payment and inventory management for small businesses. It is also cost-efficient. Because of their ease of use, blockchain platforms are now cheap to implement and can easily integrate into existing systems while bringing in value at a relatively minor cost.
What are the challenges of adopting blockchain in supply chain management?
The challenges of adopting blockchain in supply chain management include high initial costs and the complexity of integrating new technology with existing systems. Some of the challenges that may be realized in a business environment include the need to have the partners get on the same page about blockchain, which may be very hard to achieve, hence leading to the challenge of collaboration. Secondly, the expansion of the size of a blockchain network may become a problem due to the fact that the chains can start to become slower as more individuals take part in the process. There is also a need for professionals to manage and maintain the blockchain option, and this can be a result of the complexity.
How can blockchain reduce costs in supply chains?
The challenges of adopting blockchain in supply chain management include high initial costs and the complexity of integrating new technology with existing systems. Several companies may have difficulty getting all their partners to accept blockchain, which can affect coordination. Furthermore, there may be issues with scalability as more people work on the blockchain platform, resulting in slow movement. The threat of recruiting qualified employees to oversee the management and maintenance of the blockchain system can also sum up the overall challenge.
How does blockchain improve transparency in supply chain operations?
It eradicates favoritism and the black-box nature of supply chain operations by introducing a new and secure technology called blockchain. Every supplier chain can get real-time information about the flow of supplies from manufacturers to suppliers. This eliminates probable fraud and ensures that everyone is informed about the agreed means of the investment. With the help of blockchain, the business can monitor the products at different stages, providing transparency and responsibility for the actions that occur in the supply chain, which gives confidence to the suppliers, manufacturers, and customers.
How does blockchain enhance supply chain security and traceability?
Blockchain increases the security of the supply chain and tracks back each transaction to provide an untampered record of the transaction. All the movements of products result in the blockchain, so there will be a clear and very detailed history of each product, starting from the manufacturing process to distribution. This keeps the data accurate, minimizes fraud occurrences, and guarantees easy tracking of the products to their source. By offering simple real-time data updates and producing a record that cannot be altered, many companies can quickly note problems with the supply management system.










